 Although it’s widely used for chronic pain, there’s controversy as to its value.
Although it’s widely used for chronic pain, there’s controversy as to its value.
Now, researchers at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, in New York City, reviewed the evidence in 4 chronic pain conditions. Continue reading Acupuncture: Effective to treat chronic pain →
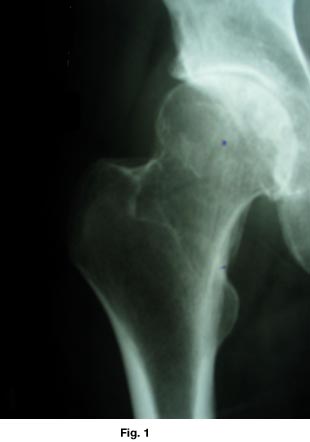 Former Medical Director, of the Rosenthal Center for Complementary & Alternative Medicine, at Columbia University Medical Center, in New York City, Dr. James Dillard, reviewed the evidence.
Former Medical Director, of the Rosenthal Center for Complementary & Alternative Medicine, at Columbia University Medical Center, in New York City, Dr. James Dillard, reviewed the evidence.
Here’s what we know. Continue reading Complementary treatments for osteoarthritis →
 Zingiber officinale, commonly known as ginger, has been used to treat pain, among other things.
Zingiber officinale, commonly known as ginger, has been used to treat pain, among other things.
Prof. Ernst and colleagues from the University of Exeter, in the UK reviewed the evidence for the use of ginger to treat any type of pain. Continue reading Review: Ginger to treat pain →
 Researchers in Germany searched the records from almost 10,000 patients for predictors of a positive response. Continue reading Predictors of a positive response to acupuncture for chronic pain →
Researchers in Germany searched the records from almost 10,000 patients for predictors of a positive response. Continue reading Predictors of a positive response to acupuncture for chronic pain →
 Prof. Ernst and a colleague critically evaluated the systematic reviews of tai chi for any improvement of medical conditions or clinical symptoms. Continue reading Reviewing the reviews of tai chi →
Prof. Ernst and a colleague critically evaluated the systematic reviews of tai chi for any improvement of medical conditions or clinical symptoms. Continue reading Reviewing the reviews of tai chi →
 Researchers at the Johns Hopkins School of Public Health, in Baltimore, Maryland, reviewed the evidence. Continue reading Review: Yoga for arthritis →
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins School of Public Health, in Baltimore, Maryland, reviewed the evidence. Continue reading Review: Yoga for arthritis →
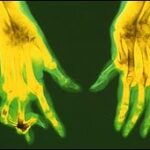 Prof. Ernst and colleague evaluated the evidence on CAM treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Continue reading Review: CAM for arthritis →
Prof. Ernst and colleague evaluated the evidence on CAM treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Continue reading Review: CAM for arthritis →
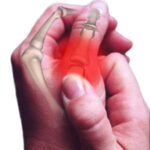 Researchers at the University of Geneva School of Medicine, in Switzerland, evaluated the response to highly purified chondroitin 4&6 sulfate (CS) in patients with hand osteoarthritis. Continue reading Symptomatic response to chondroitin in patients with osteoarthritis →
Researchers at the University of Geneva School of Medicine, in Switzerland, evaluated the response to highly purified chondroitin 4&6 sulfate (CS) in patients with hand osteoarthritis. Continue reading Symptomatic response to chondroitin in patients with osteoarthritis →
 Reduced aerobic capacity in people osteoarthritis of the lower limbs affects independence and the ability to perform everyday activities.
Reduced aerobic capacity in people osteoarthritis of the lower limbs affects independence and the ability to perform everyday activities.
Researchers at Universidad de Extremadura, in Spain, reviewed exercise programs and the ability to perform activities require sustained aerobic metabolism. Continue reading Comparing exercise programs in people with osteoarthritis →
 Researchers at the University of Siena, in Italy, evaluated whether balneotherapy (treatment of disease by baths) with mineral sulphate-bicarbonate-calcium water might achieve symptomatic improvement, and improve quality of life of patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Continue reading Effects of balneotherapy on quality of life in osteoarthritis →
Researchers at the University of Siena, in Italy, evaluated whether balneotherapy (treatment of disease by baths) with mineral sulphate-bicarbonate-calcium water might achieve symptomatic improvement, and improve quality of life of patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Continue reading Effects of balneotherapy on quality of life in osteoarthritis →
 Ginger (Zingiber officnale) exerts anti-inflammatory effects, and heat treatment of ginger has been suggested to enhance its pain relieving effects.
Ginger (Zingiber officnale) exerts anti-inflammatory effects, and heat treatment of ginger has been suggested to enhance its pain relieving effects.
Now, researchers from Georgia College and State University, in Milledgeville report the results of 2 studies in adults. Continue reading Anti-inflammatory effects of heated vs unheated ginger →
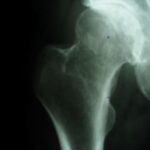 There’s a growing recognition of the importance of physical exercise to reduce pain in knee and hip joints.
There’s a growing recognition of the importance of physical exercise to reduce pain in knee and hip joints.
Researchers at Universidad de Extremadura, in Spain, compared the effectiveness of exercise programs on pain in patients with hip and knee osteoarthritis. Continue reading Exercise? Yes, but which one for osteoarthritis? →
 Moxibustion, an acupuncture-like treatment, is increasingly used in the management of rheumatic conditions.
Moxibustion, an acupuncture-like treatment, is increasingly used in the management of rheumatic conditions.
Prof. Ernst and colleagues reviewed the evidence. Continue reading Review: Moxibustion for rheumatic conditions →
 During the American College of Rheumatology Annual Scientific Meeting, researchers in Boston reported (abstract 706) that adding vitamin D as a supplement did not lessen the symptoms or slow the progression of knee osteoarthritis. Continue reading Does vitamin D reduce progression of knee osteoarthritis? →
During the American College of Rheumatology Annual Scientific Meeting, researchers in Boston reported (abstract 706) that adding vitamin D as a supplement did not lessen the symptoms or slow the progression of knee osteoarthritis. Continue reading Does vitamin D reduce progression of knee osteoarthritis? →
 The effects of tai chi on knee muscle strength, bone mineral density, and fear of falling were studied by researchers at Chungnam National University, in Daejeon, South Korea. Continue reading Tai chi effects in women with osteoarthritis →
The effects of tai chi on knee muscle strength, bone mineral density, and fear of falling were studied by researchers at Chungnam National University, in Daejeon, South Korea. Continue reading Tai chi effects in women with osteoarthritis →
 Researchers at the Universitetet i Oslo, tell us, “Since 2004, glucosamine has been available as a prescription drug [in Norway] for symptomatic treatment of mild to moderate osteoarthritis.
Researchers at the Universitetet i Oslo, tell us, “Since 2004, glucosamine has been available as a prescription drug [in Norway] for symptomatic treatment of mild to moderate osteoarthritis.
The aim of this study was evaluate the use of glucosamine on the need for analgesic drugs. Continue reading Failure of glucosamine to reduce the use of pain relieving drugs →
 Researchers in Europe reviewed the evidence for glucosamine, chondroitin, and the combination to treat osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Continue reading Review: Glucosamine, chondroitin, and osteoarthritis →
Researchers in Europe reviewed the evidence for glucosamine, chondroitin, and the combination to treat osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Continue reading Review: Glucosamine, chondroitin, and osteoarthritis →
 There’s conflicting evidence on the value of Traditional Chinese Acupuncture (TCA).
There’s conflicting evidence on the value of Traditional Chinese Acupuncture (TCA).
Now, researchers at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, in Houston report the influence of the acupuncturist on the response to treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Continue reading Influence of aucpuncturists on treatment outcomes in osteoarthritis →
Complementary and Alternative Medicine: Fair, Balanced, and to the Point
 Although it’s widely used for chronic pain, there’s controversy as to its value.
Although it’s widely used for chronic pain, there’s controversy as to its value.














