 This product, when used as directed, produces an industrial bleach that can cause serious harm.
This product, when used as directed, produces an industrial bleach that can cause serious harm.
Swallowing doses of this bleach, such as those recommended in the labeling can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and symptoms of severe dehydration. Continue reading Consumer Alert: Miracle Mineral Supplement aka MMS →
 Alternative explanations are common in about 47% of suspected drug-induced liver injury.
Alternative explanations are common in about 47% of suspected drug-induced liver injury.
Researchers in Germany raised the question of whether a similar frequency might prevail in cases of assumed herb-induced liver injury. Continue reading Profiling and assumed herb-induced liver toxicity →
 If campaigns to promote more healthful eating are ineffective, how else might society address the obesity epidemic?
If campaigns to promote more healthful eating are ineffective, how else might society address the obesity epidemic?
MailOnline reports that deportation is an option. Continue reading Too fat to live in New Zealand →
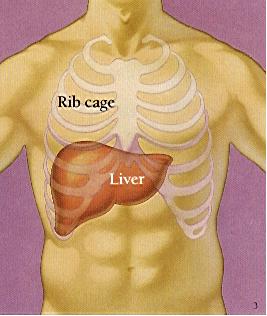 Silymarin (Silybium marianum), an extract of milk thistle, is often used to treat chronic liver disease.
Silymarin (Silybium marianum), an extract of milk thistle, is often used to treat chronic liver disease.
Researchers with the Silymarin in the NASH and C Hepatitis (SyNCH) Study Group studied its effect when combined with interferon. Continue reading Milk thistle fails in study of Hep C treatment →
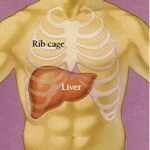 The botanical extract silymarin (milk thistle,) has anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties and is used by patients with chronic liver disease.
The botanical extract silymarin (milk thistle,) has anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties and is used by patients with chronic liver disease.
Researchers throughout the U.S. collaborated to evaluate the response to high doses of silymarin taken by mouth on disease activity in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The results were presented during the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases November Annual Meeting. Continue reading No benefit from milk thistle to treat hepatitis C →
 Researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine and Tufts Medical Center, in Boston, are the first to evaluate changes in the cholesterol-lowering effects of atorvastatin (Lipitor) in patients with high cholesterol taking stable doses atorvastatin while drinking typical quantities of grapefruit juice. Continue reading Final word on the statin-grapefruit juice interaction? →
Researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine and Tufts Medical Center, in Boston, are the first to evaluate changes in the cholesterol-lowering effects of atorvastatin (Lipitor) in patients with high cholesterol taking stable doses atorvastatin while drinking typical quantities of grapefruit juice. Continue reading Final word on the statin-grapefruit juice interaction? →
 Aromatase inhibitors are a class of drugs used to treat breast cancer and ovarian cancer in postmenopausal women.
Aromatase inhibitors are a class of drugs used to treat breast cancer and ovarian cancer in postmenopausal women.
Now, the FDA is recalling the following supplements that illegally contain these drugs. Continue reading Consumer Alert: Aromatase inhibitors in dietary supplements →
 Researchers from Italy report that low vitamin D is linked to severe fibrosis and a poor response to interferon treatment. Continue reading Low vitamin D levels lower the response to treatment of hepatitis C →
Researchers from Italy report that low vitamin D is linked to severe fibrosis and a poor response to interferon treatment. Continue reading Low vitamin D levels lower the response to treatment of hepatitis C →
 Milk thistle is often used to treat chemotherapy-associated liver toxicity.
Milk thistle is often used to treat chemotherapy-associated liver toxicity.
Researchers from the US studied it in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Continue reading Is there a role for milk thistle treatment of liver toxicity in leukemia? →
 It occurs in up to 20% of patients with cirrhosis of the liver and should be considered in anyone who develops difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
It occurs in up to 20% of patients with cirrhosis of the liver and should be considered in anyone who develops difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
In 1992, researchers from the University of Florida published a report of a patient with hepatopulmonary syndrome who failed drug therapy, refused surgery, but improved while taking garlic supplements.
Here’s the latest study from the Medical College Calcutta, in India. Continue reading Growing evidence supports garlic to treat hepatopulmonary syndrome →
 Researchers from Johann Wolfgang Goethe University of Frankfurt/Main, in Hanau, Germany, reviewed the evidence and believe the risk is less than suspected. Continue reading Re-evaluating the risk of liver toxicity from black cohosh →
Researchers from Johann Wolfgang Goethe University of Frankfurt/Main, in Hanau, Germany, reviewed the evidence and believe the risk is less than suspected. Continue reading Re-evaluating the risk of liver toxicity from black cohosh →
 This is the first reported case of a patient taking imatinib (Gleevec), which is used to treat certain cancers, who developed liver toxicity, apparently related to taking ginseng. Continue reading Imatinib liver toxicity associated with ginseng →
This is the first reported case of a patient taking imatinib (Gleevec), which is used to treat certain cancers, who developed liver toxicity, apparently related to taking ginseng. Continue reading Imatinib liver toxicity associated with ginseng →
 Do you find that you’re not getting the weight loss results you want from diet and exercise alone?
Do you find that you’re not getting the weight loss results you want from diet and exercise alone?
If you do and you tried Hydroxycut, be forewarned that this product has been associated with serious liver injury. Continue reading Consumer Alert: Hydroxycut →
 Biliary atresia is a rare disease of infants in which the flow of bile from the liver to the intestine may be blocked and requires surgery. Even after surgery, bile flow may be impaired and lead to a deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins. In this case, vitamin supplements may be needed.
Biliary atresia is a rare disease of infants in which the flow of bile from the liver to the intestine may be blocked and requires surgery. Even after surgery, bile flow may be impaired and lead to a deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins. In this case, vitamin supplements may be needed.
Researchers from Children’s Hospital Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania studied ADEKs and AquADEKs — products that contain increased amounts of fat-soluble vitamins, which are rapidly absorbed, independent of bile flow. Continue reading Two multivitamin preparations are ineffective for treating biliary atresia →
 Â The FDA warns against using products advertised as alternatives to anabolic steroids for increasing muscle mass and strength.
 The FDA warns against using products advertised as alternatives to anabolic steroids for increasing muscle mass and strength.
These products are promoted as dietary supplements to improve sports performance and aid in recovery from training and sporting events. Continue reading Consumer Alert: Sports performance supplements →
 Researchers from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland believe this is the first study of its kind.
Researchers from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland believe this is the first study of its kind.
The results were presented during the annual meeting of the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Continue reading Might exercise benefit diabetics with fatty liver? →
 Piper methysticum (kava) has been withdrawn for sale in several countries due to concerns over liver toxicity.
Piper methysticum (kava) has been withdrawn for sale in several countries due to concerns over liver toxicity.
The WHO recently recommended research into “aqueous” extracts of kava. Here are the results the Kava Anxiety Depression Spectrum Study (KADSS). Continue reading “Aqueous” extracts of kava to treat depression and anxiety →
 Â This is the third review in the past year that has come to the same conclusion.
 This is the third review in the past year that has come to the same conclusion.
This time, researchers from the Johann Wolfgang Goethe-University, in Hanau, Germany evaluated the relationship between suspected liver toxicity in 9 patients treated with black cohosh (Actaea racemosa and Cimicifuga racemosa). Continue reading The changing view of black cohosh and liver toxicity →
 Â Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a fatty inflammation of the liver that is not due to excessive alcohol use. Surprisingly, it is found in nearly one-third of urban dwelling American adults, according to 1 study.
 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a fatty inflammation of the liver that is not due to excessive alcohol use. Surprisingly, it is found in nearly one-third of urban dwelling American adults, according to 1 study.
Researchers from the Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center in Israel studied the relationship between leisure-time physical activity and NAFLD, which is often recommended as part of treatment. Continue reading Leisure activity and nonalcoholic fatty liver →
Complementary and Alternative Medicine: Fair, Balanced, and to the Point
 This product, when used as directed, produces an industrial bleach that can cause serious harm.
This product, when used as directed, produces an industrial bleach that can cause serious harm.







 Do you find that you’re not getting the weight loss results you want from diet and exercise alone?
Do you find that you’re not getting the weight loss results you want from diet and exercise alone? Biliary atresia is a rare disease of infants in which the flow of bile from the liver to the intestine may be blocked and requires surgery. Even after surgery, bile flow may be impaired and lead to a deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins. In this case, vitamin supplements may be needed.
Biliary atresia is a rare disease of infants in which the flow of bile from the liver to the intestine may be blocked and requires surgery. Even after surgery, bile flow may be impaired and lead to a deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins. In this case, vitamin supplements may be needed. Â The FDA
 The FDA  Researchers from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland believe this is the first
Researchers from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland believe this is the first  Piper methysticum (kava) has been withdrawn for sale in several countries due to concerns over liver toxicity.
Piper methysticum (kava) has been withdrawn for sale in several countries due to concerns over liver toxicity. Â This is the third review in the past year that has come to the same conclusion.
 This is the third review in the past year that has come to the same conclusion.  Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a fatty inflammation of the liver that is not due to excessive alcohol use. Surprisingly, it is found in nearly one-third of urban dwelling American adults, according to 1
 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a fatty inflammation of the liver that is not due to excessive alcohol use. Surprisingly, it is found in nearly one-third of urban dwelling American adults, according to 1