 Dietary supplement use has steadily increased since the 1970s.
Dietary supplement use has steadily increased since the 1970s.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health estimated dietary supplement use based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003–2006, a nationally representative survey. Continue reading Increasing popularity of dietary supplements →
 Dietary supplements are commonly taken to prevent chronic disease.
Dietary supplements are commonly taken to prevent chronic disease.
Researchers in Finland, Norway, and the Republic of Korea studied the long-term health consequences. Continue reading Dietary supplements and the risk of death in older women →
 FDA advises that prescription proton pump inhibitor drugs may cause low magnesium blood levels (hypomagnesemia) if taken, in most cases, longer than one year.
FDA advises that prescription proton pump inhibitor drugs may cause low magnesium blood levels (hypomagnesemia) if taken, in most cases, longer than one year.
Proton pump inhibitors reduce the amount of acid in the stomach and treat conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and inflammation of the esophagus. Continue reading Effect of proton pump inhibitors on magnesium →
 At the University of Turin, in Italy, researchers reviewed the evidence.
At the University of Turin, in Italy, researchers reviewed the evidence.
And contributors to the US Headache Consortium tell us why it’s important. Continue reading Reviewing non-pharmacological options to prevent migraine →
 Approximately 6.8 million Americans suffer from generalized anxiety disorder. It’s not surprising then that there’s interest in finding effective natural treatments.
Approximately 6.8 million Americans suffer from generalized anxiety disorder. It’s not surprising then that there’s interest in finding effective natural treatments.
The Global Neuroscience Initiative Foundation, in Los Angeles, California, reviewed the evidence for passionflower, lysine, magnesium, kava, and St John’s wort, alone or in combination. Continue reading Nutritional herbal supplements for treating anxiety →
 Researchers from Dalhousie University, in Halifax, Nova Scotia reviewed the evidence and make recommendations for women experiencing symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Continue reading Reviewing herbs, vitamins, and minerals in treating premenstrual syndrome →
Researchers from Dalhousie University, in Halifax, Nova Scotia reviewed the evidence and make recommendations for women experiencing symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Continue reading Reviewing herbs, vitamins, and minerals in treating premenstrual syndrome →
 Dr. Stewart Tepper from the Cleveland Clinic Foundation in Ohio reports that “parents frequently ask healthcare professionals to provide ‘natural’ migraine care for their children.” Continue reading Little evidence supports CAM for childhood headaches →
Dr. Stewart Tepper from the Cleveland Clinic Foundation in Ohio reports that “parents frequently ask healthcare professionals to provide ‘natural’ migraine care for their children.” Continue reading Little evidence supports CAM for childhood headaches →
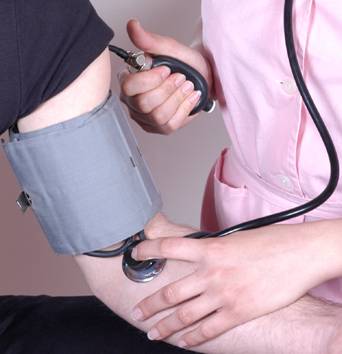 It lowered blood pressure in adults with hypertension, but not in people with normal blood pressure. Continue reading Effect of magnesium on blood pressure →
It lowered blood pressure in adults with hypertension, but not in people with normal blood pressure. Continue reading Effect of magnesium on blood pressure →
 Reviewers from The New York Headache Center concluded, “The identification of food triggers, with the help of food diaries, is an inexpensive way to reduce migraine headaches.”
Reviewers from The New York Headache Center concluded, “The identification of food triggers, with the help of food diaries, is an inexpensive way to reduce migraine headaches.”
Here’s their list of triggers and treatments. Continue reading Foods and supplements to help manage migraine →
 Dietary calcium and magnesium may protect Chinese women from developing type 2 diabetes, according to researchers at Shanghai Cancer Institute in China. Continue reading Calcium, magnesium, and the risk of type 2 diabetes →
Dietary calcium and magnesium may protect Chinese women from developing type 2 diabetes, according to researchers at Shanghai Cancer Institute in China. Continue reading Calcium, magnesium, and the risk of type 2 diabetes →
 Researchers from the University of Canterbury, at Christchurch, New Zealand reviewed the evidence supporting the use of nutritional and herbal supplements to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Continue reading Treating ADHD with supplements →
Researchers from the University of Canterbury, at Christchurch, New Zealand reviewed the evidence supporting the use of nutritional and herbal supplements to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Continue reading Treating ADHD with supplements →
 Babies born too early (preterm) have a higher risk of dying in the first weeks of life, and those who survive often have damage in the form of cerebral palsy
Babies born too early (preterm) have a higher risk of dying in the first weeks of life, and those who survive often have damage in the form of cerebral palsy
This Cochrane review identified positive effects of magnesium sulphate when given to women at risk of preterm birth. Continue reading Giving magnesium to women at risk for preterm birth →
 The Harvard Women’s Health Watch has published recommendations to lower the risk of fractures due to osteoporosis.
The Harvard Women’s Health Watch has published recommendations to lower the risk of fractures due to osteoporosis.
I supplemented their recommendations with references. Continue reading Recommendations from Harvard for bone health →
 Dr. Cathi Dennehy from the Department of Clinical Pharmacy at the University of California San Francisco has reviewed the evidence.
Dr. Cathi Dennehy from the Department of Clinical Pharmacy at the University of California San Francisco has reviewed the evidence.
I was surprised by her assessment of black cohosh for menopausal symptoms.
Here’s a summary of her findings.
Continue reading Review of herbal medicines in gynecology →
 The National Center for CAM (NCCAM) has summarized the state of the science. Continue reading The NCCAM view of CAM for fibromyalgia →
The National Center for CAM (NCCAM) has summarized the state of the science. Continue reading The NCCAM view of CAM for fibromyalgia →
 Magnesium sulfate is given to prevent seizures in pregnant women with preeclampsia (high blood pressure, edema, and protein in the urine) and to inhibit preterm labor.
Magnesium sulfate is given to prevent seizures in pregnant women with preeclampsia (high blood pressure, edema, and protein in the urine) and to inhibit preterm labor.
This Medscape report from the meeting of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine states that injections of magnesium sulfate may protect against moderate to severe cerebral palsy. Continue reading Reducing the risk of cerebral palsy with magnesium →
 Researchers from the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke in Nuthetal monitored more than 2500 adults from 1994 to 2005. Continue reading Eating cereals high in fiber and magnesium might lower the risk of type 2 diabetes →
Researchers from the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke in Nuthetal monitored more than 2500 adults from 1994 to 2005. Continue reading Eating cereals high in fiber and magnesium might lower the risk of type 2 diabetes →
 Fifteen years after enrollment of more than 600 people between 18 and 30 years of age, researchers from the Department of Preventive Medicine at the Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago report that higher magnesium intake is associated with a lower risk of the metabolic syndrome.
Fifteen years after enrollment of more than 600 people between 18 and 30 years of age, researchers from the Department of Preventive Medicine at the Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago report that higher magnesium intake is associated with a lower risk of the metabolic syndrome.
The results are interesting, but what’s the action plan for the average person?
Continue reading Magnesium and the metabolic syndrome →
 Young adults with higher magnesium intake have a lower risk of developing the metabolic syndrome. This is the conclusion from an April 2006 article published in the journal Circulation.
Young adults with higher magnesium intake have a lower risk of developing the metabolic syndrome. This is the conclusion from an April 2006 article published in the journal Circulation.
Here are the details. Continue reading Magnesium and the metabolic syndrome →
Complementary and Alternative Medicine: Fair, Balanced, and to the Point
 Dietary supplement use has steadily increased since the 1970s.
Dietary supplement use has steadily increased since the 1970s.

 Researchers from Dalhousie University, in Halifax, Nova Scotia
Researchers from Dalhousie University, in Halifax, Nova Scotia  Dr. Stewart Tepper from the Cleveland Clinic Foundation in Ohio
Dr. Stewart Tepper from the Cleveland Clinic Foundation in Ohio  It lowered blood pressure in adults with hypertension, but not in people with normal blood pressure.
It lowered blood pressure in adults with hypertension, but not in people with normal blood pressure.  Reviewers from The New York Headache Center
Reviewers from The New York Headache Center  Dietary calcium and magnesium may protect Chinese women from developing type 2 diabetes,
Dietary calcium and magnesium may protect Chinese women from developing type 2 diabetes,  Researchers from the University of Canterbury, at Christchurch, New Zealand
Researchers from the University of Canterbury, at Christchurch, New Zealand  Babies born too early (preterm) have a higher risk of dying in the first weeks of life, and those who survive often have damage in the form of cerebral palsy
Babies born too early (preterm) have a higher risk of dying in the first weeks of life, and those who survive often have damage in the form of cerebral palsy The results of this study almost support an old home remedy.
The results of this study almost support an old home remedy.  The Harvard Women’s Health Watch has
The Harvard Women’s Health Watch has  Dr. Cathi Dennehy from the Department of Clinical Pharmacy at the University of California San Francisco has reviewed the evidence.
Dr. Cathi Dennehy from the Department of Clinical Pharmacy at the University of California San Francisco has reviewed the evidence. Magnesium sulfate is given to prevent seizures in pregnant women with preeclampsia (high blood pressure, edema, and protein in the urine) and to inhibit preterm labor.
Magnesium sulfate is given to prevent seizures in pregnant women with preeclampsia (high blood pressure, edema, and protein in the urine) and to inhibit preterm labor. Researchers from the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke in Nuthetal
Researchers from the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke in Nuthetal  Fifteen years after enrollment of more than 600 people between 18 and 30 years of age, researchers from the Department of Preventive Medicine at the Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago
Fifteen years after enrollment of more than 600 people between 18 and 30 years of age, researchers from the Department of Preventive Medicine at the Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago  Young adults with higher magnesium intake have a lower risk of developing the metabolic syndrome. This is the conclusion from an April 2006
Young adults with higher magnesium intake have a lower risk of developing the metabolic syndrome. This is the conclusion from an April 2006