 Folklore remedies for pain and inflammation support these bracelets to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Folklore remedies for pain and inflammation support these bracelets to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Researchers at The University of York, in the UK studied their effects. Continue reading Static magnets and copper fail to improve arthritis
 Folklore remedies for pain and inflammation support these bracelets to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Folklore remedies for pain and inflammation support these bracelets to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Researchers at The University of York, in the UK studied their effects. Continue reading Static magnets and copper fail to improve arthritis
 Wilson disease is a genetic disorder that affects copper storage, leading to liver failure and neurologic deterioration.
Wilson disease is a genetic disorder that affects copper storage, leading to liver failure and neurologic deterioration.
Researchers at the University Hospital of Heidelberg, in Germany, studied the long-term outcomes copper chelators vs zinc salts. Continue reading Value of zinc to treat Wilson disease
 The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has ruled that within limits, copper oxide can be safely used in food supplements. Continue reading Worried about copper in your supplements?
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has ruled that within limits, copper oxide can be safely used in food supplements. Continue reading Worried about copper in your supplements?
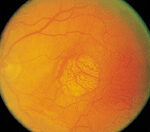 It’s a leading cause of visual loss in older adults and has limited treatment options.
It’s a leading cause of visual loss in older adults and has limited treatment options.
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health, in Bethesda, Maryland reviewed the evidence for using nutritional supplementation to treat age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Continue reading Nuritional supplements to treat age-related macular degeneration
 People tend to buy them when they’re in a lot of pain. Then, when the pain eases over time they attribute the change to the device.
People tend to buy them when they’re in a lot of pain. Then, when the pain eases over time they attribute the change to the device.
But researchers from the University of York, in the UK report they are “generally ineffective for managing pain, stiffness, and physical function in osteoarthritis.” Continue reading Ineffective magnetic bracelets
![]() Aquamin F is a plant-based source of calcium that also contains magnesium, boron, copper, and zinc.
Aquamin F is a plant-based source of calcium that also contains magnesium, boron, copper, and zinc.
In this study, it was added to ongoing osteoarthritis treatment. Continue reading Aquamin F and knee osteoarthritis
 The aim of this study was to review the literature in order to determine the levels of potentially harmful metals in table wines.
The aim of this study was to review the literature in order to determine the levels of potentially harmful metals in table wines.
We know red wine is healthy, but is it safe? Continue reading Unforeseen consequences of drinking wine
 What’s been published recently suggests there’s likely to be a problem.
What’s been published recently suggests there’s likely to be a problem.
Have we reached a tipping point? Continue reading Ayurvedic and the risk of heavy metal poisoning
 The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has ordered companies to stop marketing unapproved drug products that contain papain for topical application to the skin. Continue reading FDA acts against papain
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has ordered companies to stop marketing unapproved drug products that contain papain for topical application to the skin. Continue reading FDA acts against papain
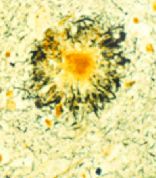
That’s fine as far as it goes, but what about those with advanced Alzheimer’s? Why not develop a more comprehensive approach?
If I might quote Paul Harvey, “here’s the rest of the story.” Continue reading Dissapointing recommendations to treat Alzheimer’s disease
 A study in northern India shows that milk fortified with specific micronutrients lowers the risk of diarrhea and acute lower respiratory illness in children.
A study in northern India shows that milk fortified with specific micronutrients lowers the risk of diarrhea and acute lower respiratory illness in children.
Here’s a list of what was added to the milk.
Continue reading Adding micronutrients to milk reduces diarrhea and respiratory illness in children

One option for treatment is chelation.
 Everybody in the west knows that lead is toxic, right? We spend lots of money removing lead paint from the walls of old houses. So, what is the logic that justifies adding lead to ayurvedic medicines?
Everybody in the west knows that lead is toxic, right? We spend lots of money removing lead paint from the walls of old houses. So, what is the logic that justifies adding lead to ayurvedic medicines?
Dr. Annapoorna Chirra from the Department of Medicine at UCLA has the answer.

Continue reading Copper, cholesterol, and Alzheimer’s disease